What is a virtual data room?
A virtual data room is a protected online platform for secure document storage, file-sharing, corporate communication, and workflow management. The solution features advanced encryption, granular user access controls, real-time activity tracking, audit logs, and customizable permissions. In addition, virtual data room software includes tools for secure document viewing, version management, bulk uploads, and integrations with other business applications.
Commonly, companies use a data room for due diligence, mergers and acquisitions, fundraising, legal transactions, and secure document sharing for audits or regulatory compliance.
Why are VDRs important for businesses today?
Virtual data rooms support faster and safer business operations by delivering the following benefits:
1. Reliable document security
Secure data room services offer advanced data protection features like watermarking, redaction, fence view, remote shredding, granular document permissions, and IP restrictions. These security measures protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches, giving businesses peace of mind in handling confidential data.
2. 24/7 data access
As cloud-based software, virtual data rooms are accessible anytime, anywhere. This round-the-clock availability ensures that users can access critical documents and collaborate without time or location constraints. In addition, most providers offer mobile apps, making it more convenient for users to work on the go.
3. Streamlined collaboration
The solution features multiple collaboration tools, including Q&A sections, document annotations, and task assignments, to help teams communicate and work more effectively. In addition, with third-party integrations, users can continue using their favourite tools within the data room platform.
4. Effective document management
VDRs offer advanced data management tools, allowing businesses to organize, search, and control access to documents easily. This way, users can quickly locate and access critical information, streamline workflows, reduce errors, and ensure that all documentation is securely stored and up-to-date.
5. Professional support
Virtual data rooms offer excellent customer support through multiple channels, including live chat, phone, and email, often with multi-language assistance. In addition, top data room providers deliver training resources and dedicated project managers to ensure smooth onboarding, assist with troubleshooting, and guide users throughout the project.
6. Cost efficiency
Although virtual data rooms may initially appear more expensive than traditional cloud storage solutions, their high-quality services justify pricing. Thus, businesses invest in top-tier security, expert support, and an exceptional user experience, gaining long-term value while minimizing the risks associated with less secure alternatives.
Main features of virtual data room
The main software tools include the following:
1. Security
- Physical data protection. Data centers utilize strict access policies, secure vaults, and uninterrupted power to protect data physically.
- Compliance. Best virtual data rooms meet rigorous global and industry-specific regulations, including ISO/IEC 27001:2013, SOC 2 & SOC 3, GDPR, and HIPAA. These certifications ensure top-tier data protection, risk management, and privacy compliance.
- Real-time data backup. Encrypted VPN tunnels provide continuous data backup, preventing document loss or destruction.
- Disaster recovery. Geographically separated data centers and emergency planning, such as fire or flood scenarios, ensure data availability in crises.
- Multi-layered data encryption. Files are transferred via TLS protocols and stored with AES 256-bit encryption. Encryption keys are securely managed separately from the data itself.
- Two-factor authentication. Secure data rooms require a password and a one-time code sent to the user’s device for extra security.
- Dynamic watermarking. Watermarks display user details, IP, and access times to identify breaches.
- Fence view. A barred viewing area prevents screenshots, screen captures, or unauthorized displays.
- Secure spreadsheet viewer. The software enables protected viewing and manipulation of Excel files, restricting formula access if necessary.
- No footprints. Secure virtual data room providers don’t store data on the user’s device; documents exist only in random access memory during viewing.
- Remote control. Administrators can remotely wipe data or shred downloaded files, revoking access even after downloads.
2. Document management
- Seamless file transfer. Users can choose between one-way or bidirectional syncing to keep local and data room folders up to date without disruptions. Syncing happens automatically at regular intervals for document consistency across platforms.
- Data room index. The software automatically organizes and categorizes all files in a virtual data room. It is continuously updated as documents are uploaded or moved, which makes files accessible and easy to search.
- Fast data upload. VDRs enable bulk uploads at high speeds. Files can be uploaded from desktops, mobile devices, and other cloud storage platforms, allowing users to add documents to a data room quickly.
- Instant search and retrieval. Users can locate specific documents quickly, using filters, keywords, and labels. Additionally, optical character recognition enables text extraction from scanned documents for better search accuracy and efficiency.
- Version control. Virtual data rooms track document versions automatically. Thus, users can manage and retrieve previous iterations, ensuring easy comparison and control over data updates.
- Document redaction. Built-in redaction tools allow users to redact sensitive information from documents before sharing, ensuring privacy and compliance.
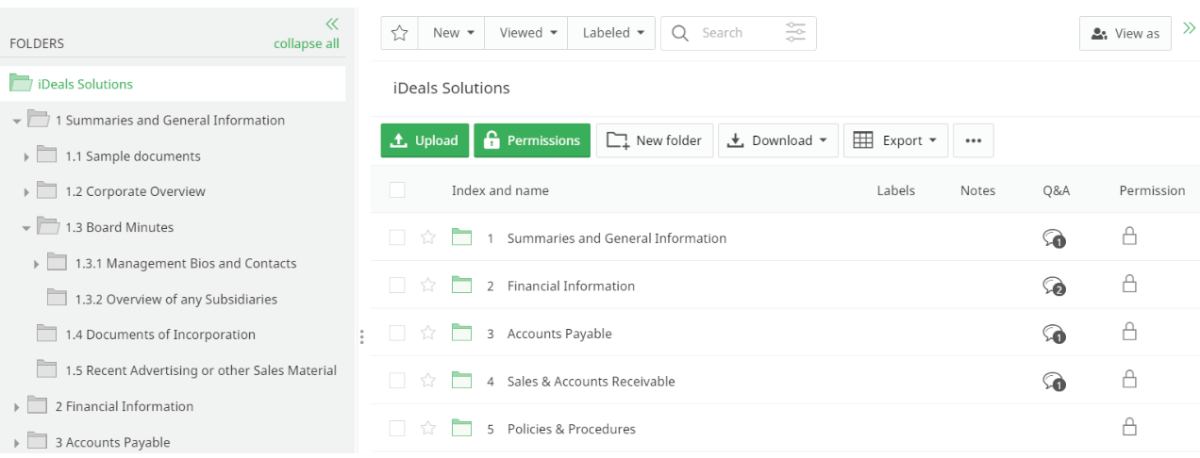
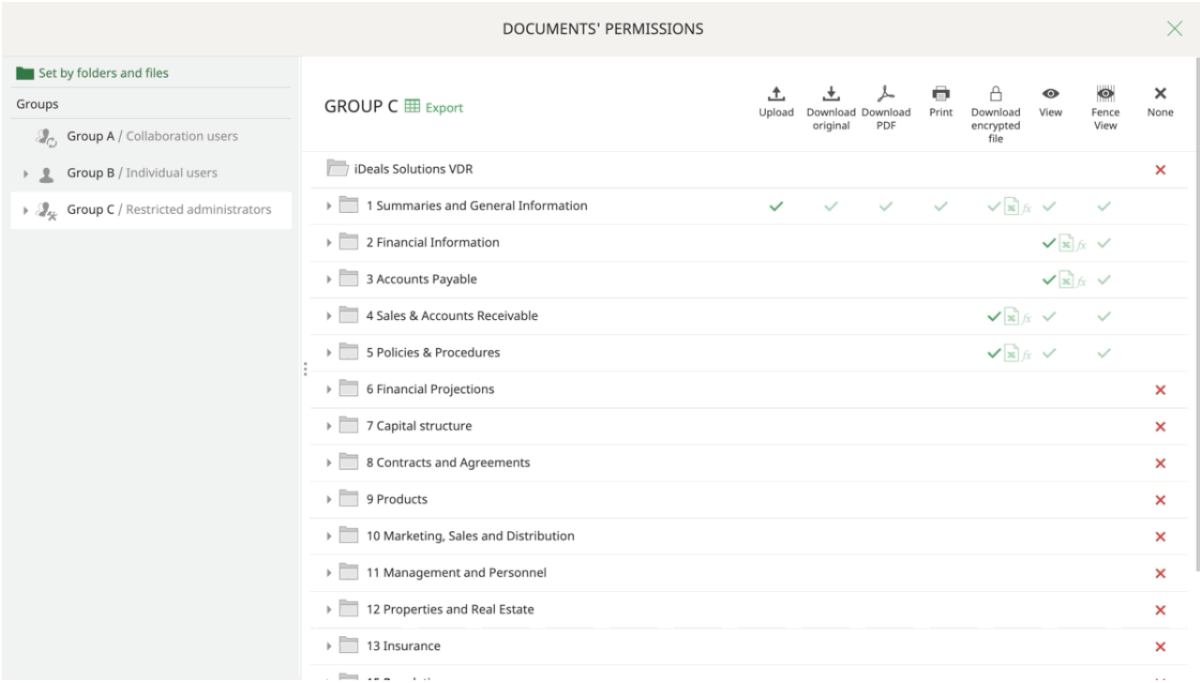
3. User management and permissions
- Centralized access control. Data room administrators can manage all access permissions from an intuitive centralized dashboard, revoking access for users in bulk or individually.
- Granular user permissions. Typically, VDR permission levels include viewing, downloading, uploading, editing, printing, and sharing. Using them, administrators can define access rights for each user based on their role.
- Document-level permissions. In addition to role-based permissions, administrators can assign access to specific folders or documents, restricting visibility and actions on a granular level.
- Time-based access. Administrators can set time-limited access for certain users, ensuring they access data rooms for the duration of a project or deal. After the expiration period, access is automatically revoked.
- Time and IP restrictions. Data rooms strengthen security by limiting when and where users access documents. In particular, administrators can set specific time frames, ensuring users can only view or download files within designated hours. IP restrictions allow access only from approved IP addresses.
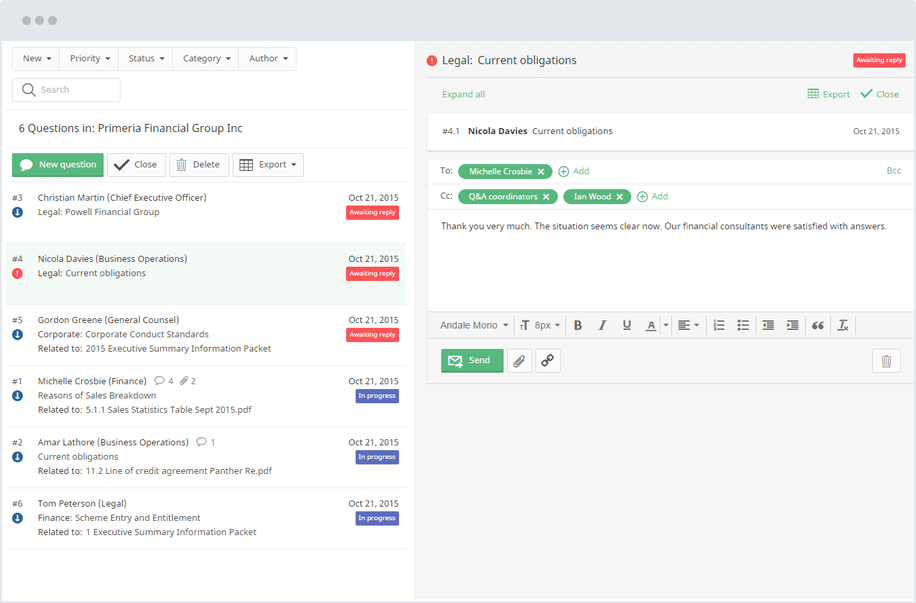
4. Communication and collaboration
- Q&A module. This dedicated communication space enables a quick exchange of questions and answers. Advanced providers allow users to submit, assign, and route questions to relevant experts manually or automatically based on predefined categories and upload questions and answers in bulk from Excel.
- Real-time notifications. Users receive instant notifications whenever new activity occurs, keeping stakeholders up-to-date.
- Commenting. Users can add comments directly on documents to foster collaboration, ask questions, or provide feedback.
- Document annotations. The software enables highlighting, underlining, and adding notes to specific sections of documents for clear review and discussion.
- Multi-project management. Teams can manage a few projects within the same platform, organizing files, tracking progress, and collaborating across deals.
- Task assignment. Data room administrators can assign tasks to other users, set deadlines, and ensure accountability for timely completion.
- Third-party integrations. The software integrates with external tools like project management software, communication platforms, and document editors for seamless workflow.
5. Analytics
- Audit trails. The software provides a full record of all user activities for accountability and compliance, including document access, edits, and downloads.
- Engagement analysis. This feature tracks how users interact with documents, including views and downloads. By analyzing these interactions, teams can identify areas of high engagement and ensure optimized collaboration efforts.
- Regular reports. Data room reports automatically summarize project activities, user engagement, and document performance at scheduled intervals. Using this data, teams can track progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions using up-to-date insights. Users can customize the frequency and type of reports they receive.
6. Usability
- Intuitive interface. User-friendly data room dashboards make it simple for users to manage documents, access key features, and collaborate, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Document previews. Users can preview documents within the platform without needing to download them. This feature improves workflow efficiency by allowing quick access to information without opening multiple files.
- Multi-language interface. A virtual data room supports multiple languages, making the solution accessible to parties from different regions and backgrounds.
- Single sign-on. Data rooms provide secure and easy access to the platform with one set of credentials, reducing the number of passwords users should remember.
- Mobile apps. Dedicated mobile apps for iOS and Android provide users with on-the-go access to a data room, allowing them to review documents, monitor activities, and collaborate from anywhere.
Use cases of virtual data rooms
1. M&A.
Data rooms for M&A simplify the deal by offering controlled access to sensitive documents, real-time updates, and audit tracking. Also, they ensure security, reduce delays, and improve collaboration during the due diligence.
2. Investment banking.
Investment banks use virtual data rooms to securely handle financial transactions, ensuring compliance, maintaining security, and providing a single platform for all stakeholders to access necessary documents quickly and efficiently.
3. IPO.
VDRs provide a secure and compliant platform for IPOs, where companies can organize sensitive documents, securely share them with regulatory bodies, and maintain complete transparency throughout the process to avoid risks of unauthorized access.
4. Litigation processes.
Data rooms securely organize case documents, ensure easy access and collaboration between legal teams, and maintain the confidentiality of sensitive materials, improving efficiency in legal proceedings.
5. Accounting.
Accounting firms benefit from VDRs as they allow secure storage and organization of financial documents, support regulatory compliance, and provide a safe collaboration platform during audits or tax preparation.
6. Real estate management.
A virtual deal room allows real estate managers to securely store and manage property documents, enabling transparent transactions and easy collaboration with brokers, buyers, and legal teams.
7. Bankruptcy and restructuring.
Virtual data rooms provide bankruptcy and restructuring teams a secure way to organize sensitive documents, manage communication with creditors, and ensure all parties involved can collaborate while maintaining confidentiality.
8. Life sciences.
The solution secures sensitive data, such as clinical trial results and patient records, and provides a compliant platform for collaboration with researchers, investors, and regulatory bodies, ensuring data protection and simplifying communication.
Virtual data room pricing
Data room pricing varies. However, providers typically use the following pricing models:
- Per page. This is good for small projects with a limited number of users and documents.
- Per user. The service price depends on how many users you expect in a deal or project.
- Data storage capacity: Some providers offer a set amount of storage (measured in GBs), which is ideal for companies with small files.
- Monthly flat rate: For projects with unpredictable needs or the need for flexibility, a monthly pricing structure is a good choice. I
- Yearly plans: Many providers offer yearly subscriptions, which are convenient for companies that regularly use data rooms.
The best virtual data room pricing structure varies based on how you plan to use it and your growth expectations.
If you manage a short-term or one-off project, flexible models like per-page or per-user pricing can minimize upfront costs. However, flat monthly rates or yearly subscriptions provide better scalability and predictability for ongoing complex transactions.
It is also worth considering hybrid options, where vendors tailor pricing based on storage, users, and feature needs. That ensures you only pay for what you use while allowing room for adjustments as your requirements change.
Why do you need a free trial?
A free trial is a limited-time opportunity provided by virtual data room providers that allows potential users to explore the platform’s features and usability before making a purchase decision. Typically, free trials last between 7 to 30 days, depending on the vendor.
In particular, a free trial is essential when conducting a virtual data room comparison because it allows you to evaluate the platform’s features, usability, and performance firsthand. By testing the solution, you can determine whether it offers the functionality required for your projects. This hands-on experience helps you make a more informed decision before committing to a purchase.











